Introduction
Since 2018, copebit has specialized in building container-based application platforms using Docker, Kubernetes, and ECS. This extensive experience has demonstrated how containerization significantly enhances both agility and security in cloud-native engineering.
As these platforms grew in complexity, we adopted DevSecOps practices to foster shared responsibility between infrastructure and application teams. Our approach has always been rooted in full automation and infrastructure-as-code (IaC). Initially, we managed infrastructure with Terraform and relied on push-based Continuous Deployment pipelines. However, at scale, the limitations of expansive Terraform stacks and intricate CD mechanisms became evident.
To regain speed, security, and simplicity, we transitioned to a GitOps approach utilizing FluxCD. This shift enabled highly automated and auditable deployments, facilitating incremental changes with minimal risk. Furthermore, GitOps has become a cornerstone of our Platform Engineering strategy.
This transition also allowed us to decouple our AWS infrastructure stack from the underlying Kubernetes stack. This separation streamlined our Terraform code, reducing external dependencies and the need for additional providers.
Technology Stack & Architecture
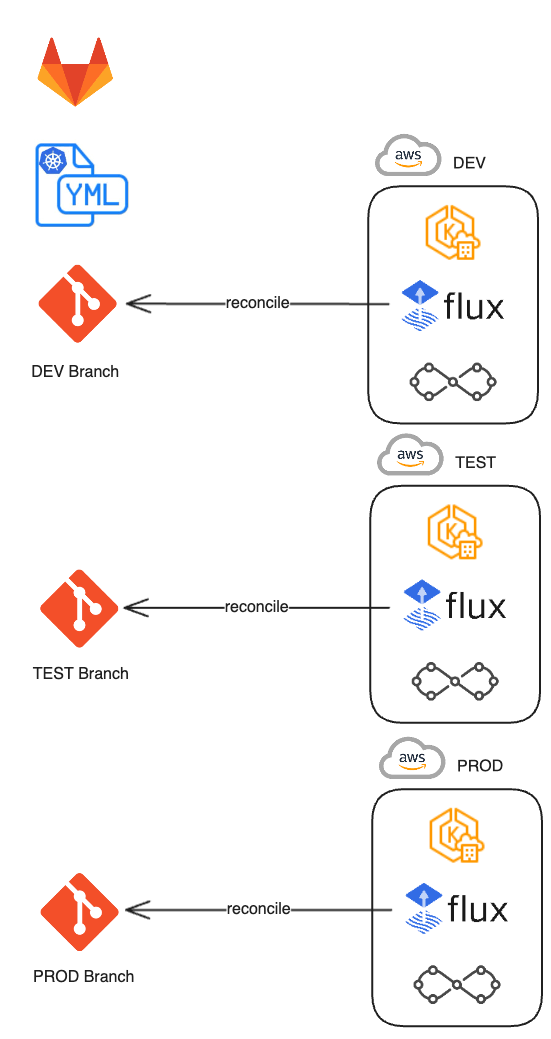
GitOps with FluxCD
FluxCD treats Git as the single source of truth for both infrastructure and application configuration. It continuously monitors Git repositories and enforces the desired state on Kubernetes, offering declarative, auditable, and immutable deployments.
This creates a so-called immutability firewall—only deployments through Git are allowed, eliminating manual drift and promoting consistency.
We recommend using stable Git platforms like GitLab.com or GitHub.com, though self-hosted solutions are equally supported.
Demo: Streamlining Kubernetes Resource Management with FluxCD
This brief demonstration illustrates the process of adding a new FluxCD resource—specifically, a basic Kubernetes namespace—to an existing FluxCD repository using GitOps.
Upon pushing the new file to version control, we observe through kubectl get ns -w that FluxCD immediately reconciles the cluster and creates the new resource.
Secure Operations & Developer Workflow
Pull-Based, Private Cluster Deployment
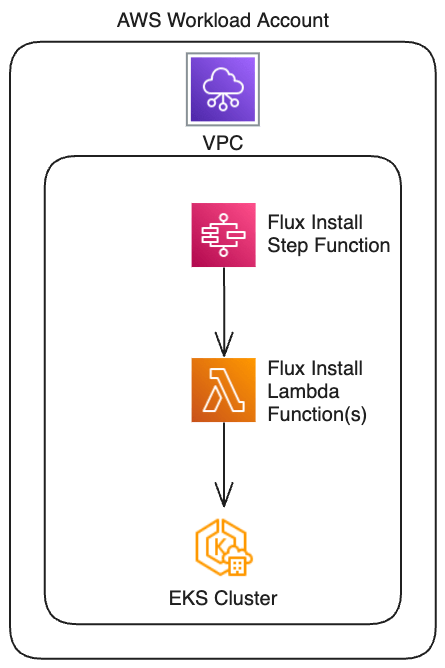
FluxCD operates as a Kubernetes controller within the cluster—no exposed endpoints are needed. copebit deploys FluxCD into fully private EKS clusters using a VPC‑attached AWS Lambda function that executes the FluxCD install command—securely and autonomously.
Sensitive information is secured using AWS Secrets Manager, ensuring secrets are robustly protected and auditable.
This pattern means DevOps teams only securely interact through Git, not the cluster—enabling minimal privilege and maximum security. Cluster-Admin roles for people can be eliminated in the best case.
Immutability and Continuous Sync
FluxCD runs with elevated cluster permissions, continuously reconciling the cluster state to match Git. Any unauthorized or manual cluster change is automatically reverted.
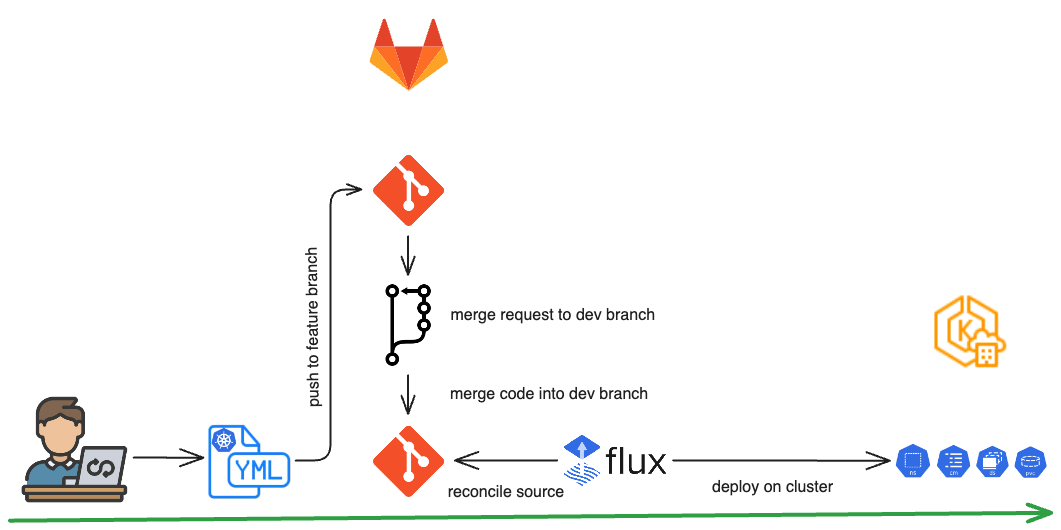
Native Developer Experience
Developers use familiar tools—committing changes to Git, going through pull requests, review processes and merging. FluxCD picks up the changes and applies them to the cluster automatically. Git branching strategies allow progressive rollout across environments in EKS.
Demonstration: Modifying an Existing Helm Release
In our next demonstration, we will modify an existing Deployment by increasing the replica count from one to two. Within a few seconds, FluxCD will reconcile the Kubernetes resource, prompting the cluster to launch an additional pod.
Deployment Options & Implementation Blueprint
FluxCD, like other GitOps tools, supports a wide array of artifacts—Kubernetes manifests, Helm charts, Kustomize overlays, Helm and OCI registries.
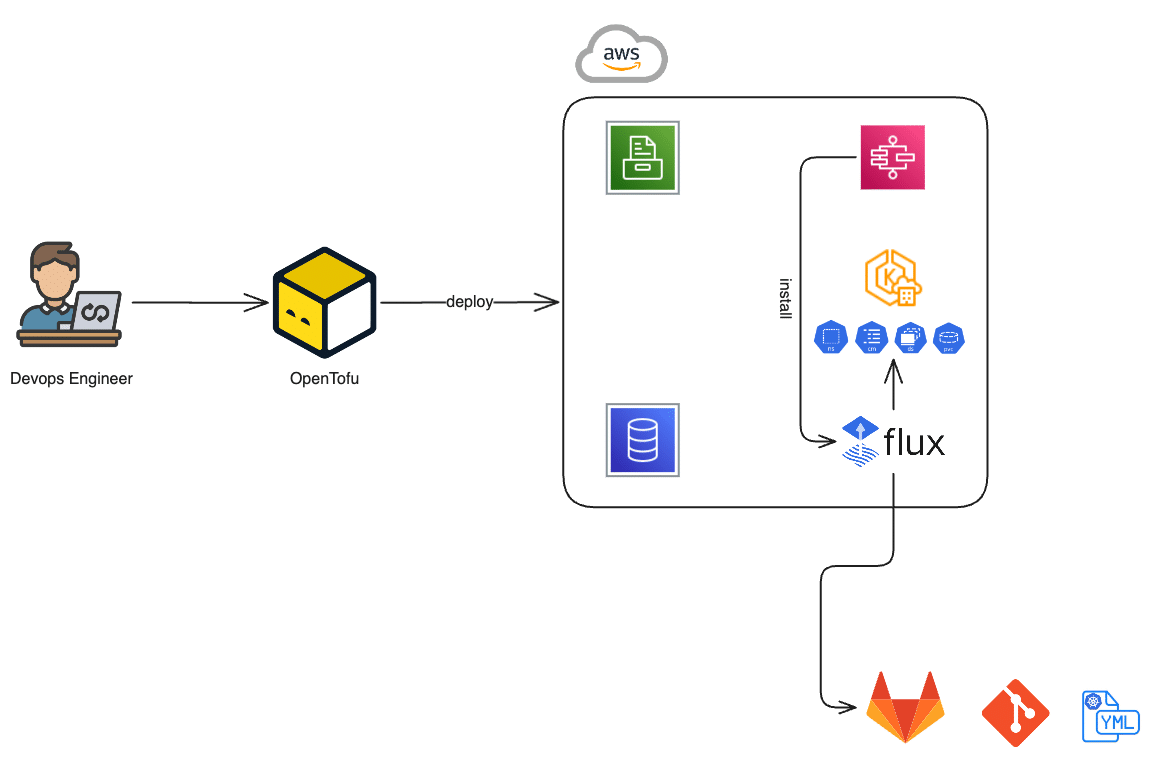
Here’s our deployment blueprint:
- Infrastructure provisioning – We define infrastructure via OpenTofu (Terraform‑compatible IaC).
- Cluster bootstrapping – A VPC‑attached Lambda function securely installs FluxCD on the private EKS cluster.
- Helm chart repository setup – A Git repository hosts copebit‑maintained, battle-tested Helm charts-including around 15 core services (e.g., external‑secrets support, block & file storage, secret controllers, Kyverno admission controls, and more).
- Application integration – Customer application repositories are integrated independently, enabling modular deployments.
All OpenTofu IaC code and Helm charts reside under version control and are protected by automated testing to ensure dependable deployment pipelines.
Benefits of using FluxCD as your GitOps tool
Key Advantages
- GitOps-driven consulting — We implement end-to-end cloud-native platforms with IaC and FluxCD.
- Secure delivery by default — No cluster exposure; all changes go through Git.
- Production-grade pipelines — Full-stack CI/CD, secure workflows, observability all integrated.
- Transparent, version-controlled assets — From infrastructure to architecture diagrams.
- Experienced delivery software — Proven success in enterprise AWS GitOps adoptions, ensuring repeatability and reliability.
Demo: Using Flux to Reconcile and Clean Up Resources
Next, we will delete the previously created FluxCD namespace and push these changes to the repository. FluxCD will then reconcile the cluster and delete the corresponding Kubernetes resource.
Summary
Shifting to GitOps with FluxCD—and coupling it with VPC‑attached Lambda‑driven bootstrap on private EKS clusters—has transformed how we deliver infrastructure and applications. Our platform now delivers declarative, secure, scalable, and auditable deployments, fully aligned with Platform Engineering best practices.
Let us help you modernize your Continuous Delivery with a GitOps-first, security-minded architecture.